How to Create a Customer Feedback Strategy (Step by Step)

After all the effort, time, and money you spend developing and marketing your product, a customer feedback strategy will help guide you on your next moves.
You see, product development is a lot like playing chess. You need to stay one step ahead of the game to deliver the features that your customers want. Sometimes, even before they know they want them.
Lets take a look at how to create a winning customer feedback strategy for your business.
What is a customer feedback strategy?
A customer feedback strategy is a process of gathering feedback from the people using your products and then acting on that feedback. There are many ways to gather feedback. You can simply ask them via surveys or monitor their behavior. Keep reading for a detailed guide on how to create your own customer feedback strategy.
Why do you need a customer feedback strategy?
A customer feedback strategy provides the data and confidence to steer the company in the right direction. Without it, you would have to make assumptions about the features that you think users want. It’s also a great way to gather ideas for improving your product. From there, you can figure out the best features to add depending on how long it will take to build, whether or not your competitors have the feature, or what you anticipate will be the next need.

Qualitative vs. quantitative customer feedback
There are two valuable types of data important to your customer feedback strategy–qualitative and quantitative.
Qualitative methods record customers’ opinions and reactions from focus groups, open-ended survey questions, and social media comments. Once you have gathered data, look for patterns in responses and determine the most common themes. While analyzing qualitative data can be complicated, it provides a deeper understanding of customers’ needs and motivations.
 Quantitative data records number of clicks on an ad, number of people who purchase an item from an ad, or number of people who opened your latest newsletter for example. Quantitative data is great for predicting what a large number of customers will do based on a smaller group’s behavior.
Quantitative data records number of clicks on an ad, number of people who purchase an item from an ad, or number of people who opened your latest newsletter for example. Quantitative data is great for predicting what a large number of customers will do based on a smaller group’s behavior.
Create customer feedback surveys
Since customers are most likely to answer surveys when they are either very satisfied or very dissatisfied, responses tend to be low and skewed. This is where Customer Satisfaction Scores and Net Promoter Scores come in. They are quick ways to gather customer feedback, increasing the likelihood of customer participation.
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score
The customer satisfaction (CSAT) score measures your customers’ satisfaction with a singular interaction, usually a customer service interaction. For example, customers may rate their satisfaction with customer service before hanging up from a phone call or disconnecting from an online chat. Companies may also follow up with a text message requesting a rating on their experience.
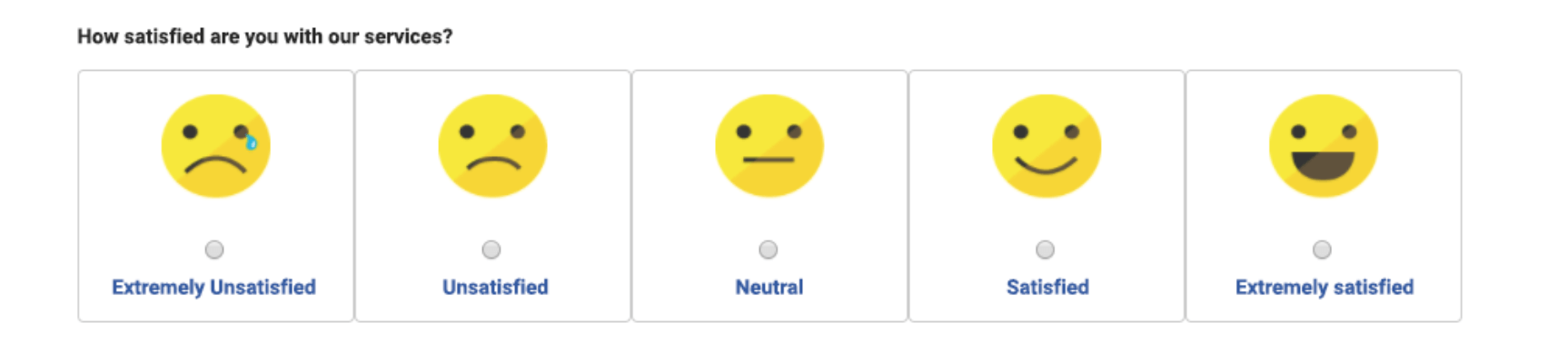
You can use a tool such as QuestionPro to help you create highly engaging surveys like the example above. Keep in mind that CSAT scores, while an important metric to track, are not perfect. For example, customers may report a less than perfect score on a customer service experience because they are reluctant to give perfect scores in general. Knowing CSAT scores will help you get an overall look at the health of your customer’s satisfaction, but it’s up to you to dig deeper.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is another quantitative approach that provides general satisfaction data about your company or product. The NPS is tabulated by asking customers “How likely are you to recommend our company to a friend or colleague?” then subtracting the percent who would not recommend the company from the percent who would recommend the company (promoters).

This question is valuable because customers are likely to answer a single question and it results in quantifiable data. However, a customer’s answer may be subject to how they are feeling at a given time, how they feel about their most recent interaction with your company, and how their cultural background influences their answer.
Customer Feedback Survey Questions
Creating a more traditional user feedback survey provides an opportunity to collect both quantitative and qualitative information. In addition to asking for a level of satisfaction, open-ended questions provide customers an opportunity to express opinions you may not have considered before.
Here are some open-ended questions that provide valuable answers:
- If you had a magic wand, what would you make this product do differently?
- Which feature caused you to choose this product above other brands?
- What is the main need that led you to purchase this product?
Create Split Tests
A third quantitative test is split testing. With split testing or A/B testing, customers are presented with two versions of a test item. For example, half of the customers may see version A of your website and the other half may see version B. The version that leads the most users to perform the action you want (such as purchase your product) has a higher conversion rate. You would then apply the version with the highest conversion rate to all target customers and split test against another version. Continuous improvement is the name of the game here.
Duolingo, for example, uses A/B testing to improve their learners’ experience. They present lessons in two versions to groups of users then compare quiz results. The lessons with the higher success rate on quizzes are distributed to the next group of users who access that lesson.
Because A/B testing can be tricky to deploy use tools offered by Optimizely or Crazy Egg. Both websites allow you to create variations, set goals, run tests, and analyze data.
Listen to your customers
Listening is a key component of gathering qualitative data. Currently, one of the best and cheapest ways to listen to your customer is through social media.
Social media monitoring
While customers may not be willing to complete a survey to provide formal feedback, many customers rarely hesitate to discuss–positively or negatively–a company on their favorite social media site. Use a tool such as BuzzSumo to track your product’s social media mentions. BuzzSumo will alert you within two hours of when your company has been acknowledged online. They can also show your sharing activity on multiple social media platforms including Facebook, Google Plus, Twitter, and Pinterest.
Collect survey answers
Just as there are many ways to gather information, there are multiple platforms for collecting survey information. Surveys can be distributed through email, social media sites, apps, in-person questionnaires for target customer groups, or QR codes at the bottom of a receipt. Choose a method based on the type of information you are wanting to gather, size of the response you would like, and your proximity to your customers.
Analyze the data
Once you have collected responses, you must interpret the data so that you can decide how to act on the feedback.
Categorize customer feedback
One way to make sense of the data you receive is to look for themes and categorize responses. Perhaps you have received multiple comments indicating that your checkout process is difficult or that product descriptions are vague. Sorting the comments you have received into categories allows you to quantify your results and recognize the most popular comments.
Implement the features
A pattern of negative comments or suggested improvements should motivate you to make changes quickly. Implementing changes based on customer feedback improves your customers’ satisfaction and creates a reputation for being responsive to customer opinions.
Feature prioritization matrix
Unfortunately, you do not have an endless supply of time, money, and resources to immediately make every change your customers’ feedback indicates need to be made. Additionally, competing opinions from the product development team and management complicate the decision.
Creating a feature prioritization matrix can guide you in making the best decision for your company and build consensus among all decision-makers.
To create a feature prioritization matrix, begin by creating a matrix with an x and y-axis.
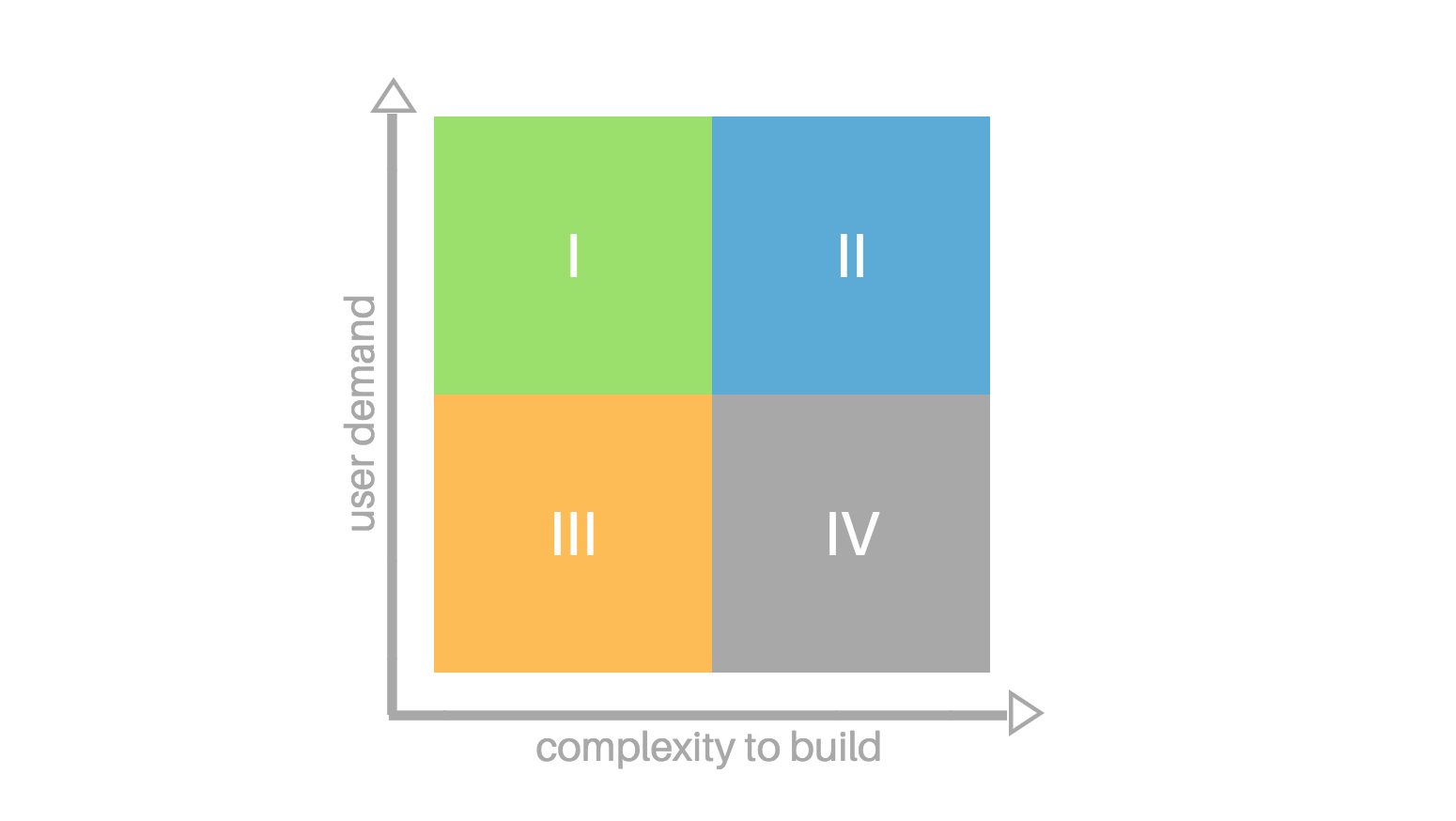 Plot business value on the x-axis and complexity on the y-axis. You will end up with the following four quadrants listed in the order that you should implement the ideas in that quadrant:
Plot business value on the x-axis and complexity on the y-axis. You will end up with the following four quadrants listed in the order that you should implement the ideas in that quadrant:
- High user demand /Low complexity (Quadrant I) – These are easy wins for you and your customers. They are easy to produce and high impact on customer experience.
- High user demand/High complexity (Quadrant II) – These features are considered second. They are more difficult to produce than those in the previous quadrant but still impact business.
- Low user demand/Low complexity (Quadrant III) – These are features that may be considered later but are not a high priority. They may be easier to make but do not have a high business impact.
- Low user demand/High complexity (Quadrant IV) – These features should be considered last. They are low impact and more difficult to develop.
You can then create the same matrix, but change the X-axis to “competition.”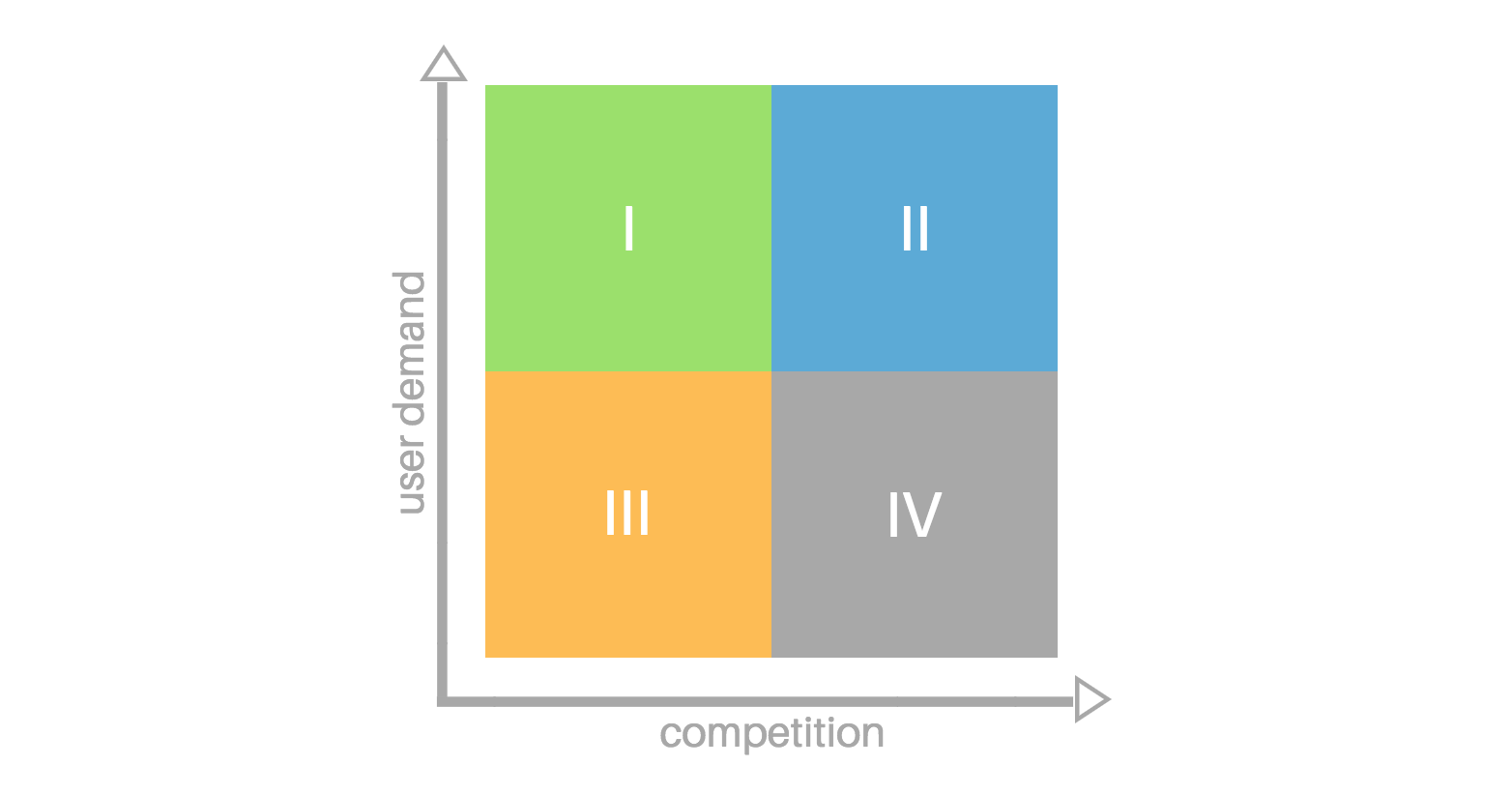
Ultimately, you want to focus first on features that are high demand, low competition, and low complexity to build.
Whichever approach you choose, developing a customer feedback strategy creates clarity and consensus in product development. Select methods based on the data you want to gather and use the best tools to make gathering data easier. Then implement the changes based on which changes have the largest impact and quickest development. Finally, feel confident in knowing that your process will prove that you are responsive to your customers’ needs.





